- About Discovery
- Discovery Prerequisites
- Preferred Management IP Address
- Discovery Configuration Guidelines and Limitations
- Discover Your Network Using CDP
- Discover Your Network Using an IP Address Range
- Discover Your Network Using LLDP
- Manage Discovery Jobs
- Stop and Start a Discovery Job
- Clone a Discovery Job
- Delete a Discovery Job
- View Discovery Job Information
- Design a New Network Infrastructure
- About Network Hierarchy
- Guidelines for Image Files to Use in Maps
- Create a Site in a Network Hierarchy
- Add a Building
- Add a Floor to a Building
- Upload an Existing Site Hierarchy
- Export Maps Archive
- Guidelines for Placing Access Points
- Add, Position, and Delete APs
- Quick View of APs
- Guidelines for Placing Inclusion and Exclusion Areas on a Floor Map
- Define an Inclusion Region on a Floor
- Define an Exclusion Region on a Floor
- Edit Location Regions
- Delete Location Regions
- View Options for Access Points
- View Options for Sensors
- View Options for Overlay Objects
- Configure Map Properties
- Configure Global Map Properties
- About Inventory
- Update the Device Polling Interval
- Display Information About Your Inventory
- Delete a Network Device
- Configure Authentication and Policy Servers
- Disable Cisco AI Network Analytics Data Collection
Set Up Cisco DNA Center to Use Assurance
Before you begin using the Assurance application, you must configure Assurance . This chapter provides the basic tasks you must do to set up Assurance . Use this chapter in conjunction with the Cisco Digital Network Architecture Center User Guide.
Limitations and Restrictions
Assurance is not supported over NATed connections to managed devices.
Basic Setup Workflow
Before you begin using the Assurance application, you must set up Cisco DNA Center to use Assurance .
See the following illustration and the procedure that follows to understand the basic workflow.
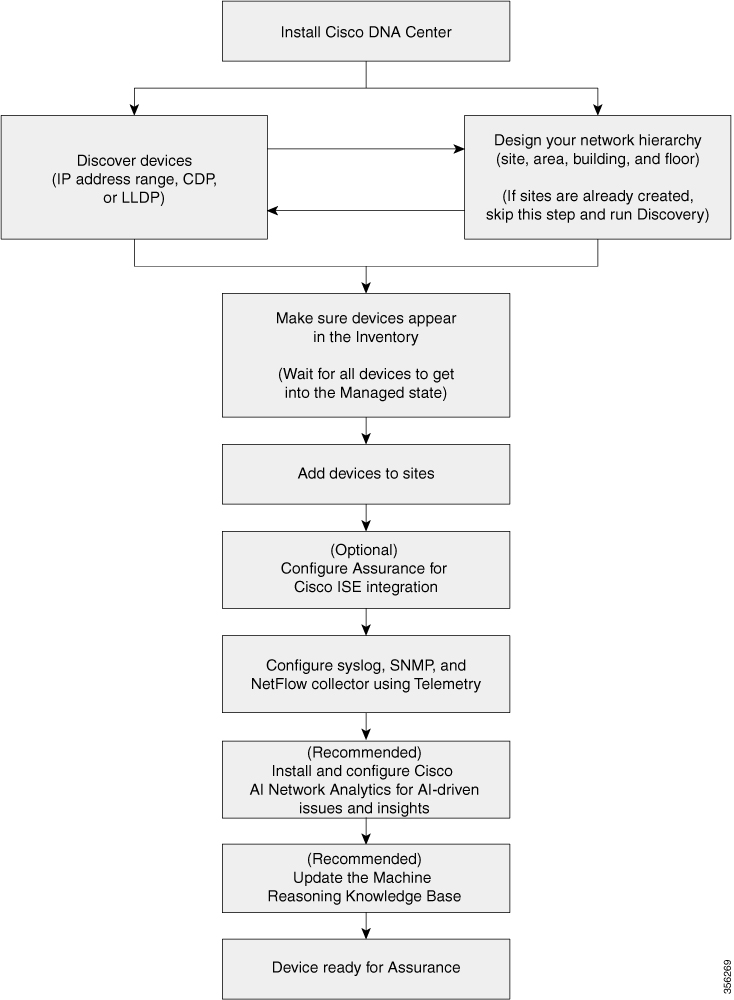
Before you begin
Procedure
Install Cisco DNA Center .
Do the following in any order:
Note Cisco Wireless Controllers must be discovered using the Management IP address instead of the Service Port IP address. If not, the related wireless controller 360 and AP 360 pages will not display any data. Note If sites are already created, you can skip this step and run Discovery. Make sure that the devices appear in the device Inventory.
You must wait for all the devices to get into a Managed state.
Add devices to sites.
If you are adding APs, we recommend that you assign and position them on a floor map.
If your network uses Cisco Identity Services Engine for user authentication, you can configure Assurance for Cisco ISE integration. This enables you to see more information about wired clients, such as the username and operating system, in Assurance .
Configure the syslog, SNMP traps, and NetFlow Collector servers using Telemetry.
(Recommended) To view AI-driven issues and gain network insights, configure Cisco AI Network Analytics data collection.
(Recommended) To have access to the latest Machine Reasoning workflows, update the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base.
Start using the Assurance application.
Discover Devices
The Discovery feature scans the devices in your network and sends the list of discovered devices to Inventory.
About Discovery
The Discovery feature scans the devices in your network and sends the list of discovered devices to Inventory.
The Discovery feature also can work with the Device Controllability feature to configure the required network settings on devices, if these settings are not already present on the device.
There are three ways for you to discover devices:
- Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) and provide a seed IP address.
- Specify a range of IP addresses. (A maximum range of 4096 devices is supported.)
- Use Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) and provide a seed IP address.
When configuring the Discovery criteria, remember that there are settings that you can use to help reduce the amount of time it takes to discover your network:
- CDP Level and LLDP Level : If you use CDP or LLDP as the Discovery method, you can set the CDP or LLDP level to indicate the number of hops from the seed device that you want to scan. The default, level 16, might take a long time on a large network. So, if fewer devices have to be discovered, you can set the level to a lower value.
- Subnet Filters : If you use an IP address range, you can specify devices in specific IP subnets for Discovery to ignore.
- Preferred Management IP : Whether you use CDP, LLDP, or an IP address range, you can specify whether you want Cisco DNA Center to add any of the device's IP addresses or only the device's loopback address.
NoteFor Cisco SD-Access Fabric and Cisco DNA Assurance , we recommend that you specify the device's loopback address. Regardless of the method you use, you must be able to reach the device from Cisco DNA Center and configure specific credentials and protocols in Cisco DNA Center to discover your devices. These credentials can be configured and saved in the Design > Network Settings > Device Credentials window or on a per-job basis in the Discovery window.
If a device uses a first hop resolution protocol like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) or Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), the device might be discovered and added to the inventory with its floating IP address. Later, if HSRP or VRRP fails, the IP address might be reassigned to a different device. This situation can cause issues with the data that Cisco DNA Center retrieves for analysis.
Discovery Prerequisites
Before you run Discovery, complete the following minimum prerequisites:
- Understand what devices will be discovered by Cisco DNA Center by viewing the Supported Devices List.
- Understand that the preferred network latency between Cisco DNA Center and devices is 100 ms round-trip time (RTT). (The maximum latency is 200 ms RTT.)
- Ensure at least one SNMP credential is configured on your devices for use by Cisco DNA Center . At a minimum, this can be an SNMPv2C read credential.
- Configure SSH credentials on the devices you want Cisco DNA Center to discover and manage. Cisco DNA Center discovers and adds a device to its inventory if at least one of the following criteria is met:
- The account that is being used by Cisco DNA Center to SSH into your devices has privileged EXEC mode (level 15).
- You configure the device’s enable password as part of the CLI credentials configured in the Discovery job. For more information, see Discovery Configuration Guidelines and Limitations.
Preferred Management IP Address
When Cisco DNA Center discovers a device, it uses one of the device's IP addresses as the preferred management IP address. The IP address can be that of a built-in management interface of the device, another physical interface, or a logical interface such as Loopback0. You can configure Cisco DNA Center to use the device's loopback IP address as the preferred management IP address, provided the IP address is reachable from Cisco DNA Center .
When you choose Use Loopback IP as the preferred management IP address, Cisco DNA Center determines the preferred management IP address as follows:
- If the device has one loopback interface, Cisco DNA Center uses that loopback interface IP address.
- If the device has multiple loopback interfaces, Cisco DNA Center uses the loopback interface with the highest IP address.
- If there are no loopback interfaces, Cisco DNA Center uses the Ethernet interface with the highest IP address. (Subinterface IP addresses are not considered.)
- If there are no Ethernet interfaces, Cisco DNA Center uses the serial interface with the highest IP address.
After a device is discovered, you can update the management IP address from the Inventory window.
Discovery Configuration Guidelines and Limitations
The following are the guidelines and limitations for Cisco DNA Center to discover your Cisco Catalyst 3000 Series Switches and Catalyst 6000 Series Switches:
- Configure the CLI username and password with privileged EXEC mode (level 15). This is the same CLI username and password that you configure in Cisco DNA Center for the Discovery function. Cisco DNA Center requires the highest access level to the device.
- Explicitly specify the transport protocols allowed on individual interfaces for both incoming and outgoing connections. Use the transport input and transport output commands for this configuration. For information about these commands, see the command reference document for the specific device type.
- Do not change the default login method for a device's console port and the VTY lines. If a device is already configured with a AAA (TACACS) login, make sure that the CLI credential defined in the Cisco DNA Center is the same as the TACACS credential defined in the TACACS server.
- Cisco Wireless Controllers must be discovered using the Management IP address instead of the Service Port IP address. If not, the related wireless controller 360 and AP 360 pages will not display any data.
Discover Your Network Using CDP
You can discover devices using Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), an IP address range, or LLDP. This procedure shows you how to discover devices and hosts using CDP. For more information about the other discovery methods, see Discover Your Network Using an IP Address Range and Discover Your Network Using LLDP.
- The Discovery function requires the correct SNMP Read Only (RO) community string. If an SNMP RO community string is not provided, as a best effort, the Discovery function uses the default SNMP RO community string, public.
- CLI credentials are not required to discover hosts; hosts are discovered through the network devices to which they are connected.
Before you begin
- Enable CDP on your network devices.
- Configure your network devices, as described in Discovery Prerequisites.
- Configure your network device's host IP address as the client IP address. (A host is an end-user device, such as a laptop computer or mobile device.)
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click Add Discovery .
In the Discovery Name field, enter a name.
Expand the IP Address/Range area if it is not already visible, and configure the following fields:
- For Discovery Type , click CDP .
- In the IP Address field, enter a seed IP address for Cisco DNA Center to start the Discovery scan.
- (Optional) In the Subnet Filter field, enter an IP address or subnet to exclude from the Discovery scan. You can enter addresses either as an individual IP address ( x.x.x.x ) or as a classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) address ( x.x.x.x/y ) , where x.x.x.x refers to the IP address and y refers to the subnet mask. The subnet mask can be a value from 0 to 32.
- Click + . Repeat Step c and Step d to exclude multiple subnets from the Discovery job.
- (Optional) In the CDP Level field, enter the number of hops from the seed device that you want to scan. Valid values are from 1 to 16. The default value is 16. For example, CDP level 3 means that CDP will scan up to three hops from the seed device.
- For Preferred Management IP , choose one of the following options:
- None : Allows the device to use any of its IP addresses.
- Use Loopback IP : Specify the device's loopback interface IP address.
Note If you choose Use Loopback IP and the device does not have a loopback interface, Cisco DNA Center chooses a management IP address using the logic described in Preferred Management IP Address. Note To use the loopback interface IP address as the preferred management IP address, make sure that the CDP neighbor's IP address is reachable from Cisco DNA Center . Expand the Credentials area and configure the credentials that you want to use for the Discovery job.
Choose any of the global credentials that have already been created or configure your own Discovery credentials. If you configure your own credentials, you can save them only for the current job by clicking Save or you can save them for the current and future jobs by checking the Save as global settings check box and then clicking Save .
- Make sure that the global credentials that you want to use are selected. If you do not want to use a credential, deselect it.
- To add additional credentials, click Add Credentials .
- To configure CLI credentials, configure the following fields:
Table 1. CLI Credentials
Field Description Name/Description Name or phrase that describes the CLI credentials. Username Name that is used to log in to the CLI of the devices in your network. Password Password that is used to log in to the CLI of the devices in your network. For security reasons, re-enter the password as confirmation. Note Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration. Note Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration. Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Name/Description : Name or description of the SNMPv2c settings that you are adding.
- Write Community : Write community string used to make changes to the SNMP information on the device.
Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Authentication type to be used. (Enabled if you select AuthPriv or AuthNoPriv as the authentication mode.) Choose one of the following authentication types:
- SHA : Authentication based on HMAC-SHA.
- MD5 : Authentication based on HMAC-MD5.
SNMPv3 password used for gaining access to information from devices that use SNMPv3. These passwords (or passphrases) must be at least eight characters in length.
- Some wireless controllers require that passwords (or passphrases) be at least 12 characters long. Be sure to check the minimum password requirements for your wireless controllers. Failure to ensure these required minimum character lengths for passwords results in devices not being discovered, monitored, or managed by Cisco DNA Center .
- Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Privacy type. (Enabled if you select AuthPriv as the authentication mode.) Choose one of the following privacy types:
- AES128 : CBC mode AES for encryption.
- None : No privacy.
SNMPv3 privacy password that is used to generate the secret key for encrypting messages that are exchanged with devices that support AES128 encryption. Passwords (or passphrases) must be at least eight characters long.
- Some wireless controllers require that passwords (or passphrases) be at least 12 characters long. Be sure to check the minimum password requirements for your wireless controllers. Failure to ensure these required minimum character lengths for passwords results in devices not being discovered, monitored, or managed by Cisco DNA Center .
- Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Table 4. SNMP Properties
Field Description Retries Number of times Cisco DNA Center tries to communicate with network devices using SNMP. Timeout Number of seconds between retries. - Name/Description : Name or description of the HTTPS credentials that you are adding.
- Username : Name used to authenticate the HTTPS connection.
- Password : Password used to authenticate the HTTPS connection. Passwords are encrypted for security and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Port : Number of the TCP/UDP port used for HTTPS traffic. The default is port number 443 (the well-known port for HTTPS).
The password must contain from 7 to 128 characters, including at least one:
- Lowercase letter (a - z)
- Uppercase letter (A - Z)
- Number (0 - 9)
- Special character: # _ * ? –
The password cannot contain spaces or angle brackets (< >). Note that some Cisco IOS XE devices do not allow a question mark (?).
You can configure up to 10 HTTPS write credentials:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the HTTPS credentials that you are adding.
- Username : Name used to authenticate the HTTPS connection.
- Password : Password used to authenticate the HTTPS connection. Passwords are encrypted for security and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Port : Number of the TCP/UDP port used for HTTPS traffic. The default is port number 443 (the well-known port for HTTPS).
The password must contain from 7 to 128 characters, including at least one:
- Lowercase letter (a - z)
- Uppercase letter (A - Z)
- Number (0 - 9)
- Special character: # _ * ? –
The password cannot contain spaces or angle brackets (< >). Note that some Cisco IOS XE devices do not allow a question mark (?).
- 830 (the default port number)
- Any other port that is available on the device
- A custom port that Cisco DNA Center configures (if Device Controllability is enabled)
NETCONF provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete configurations of network devices. NETCONF will be disabled if you choose Telnet in the Advanced area.
To configure the protocols to be used to connect with devices, expand the Advanced area and do the following tasks:
- Click the names of the protocols that you want to use. A green check mark indicates that the protocol is selected. Valid protocols are SSH (default) and Telnet .
- Drag and drop the protocols in the order that you want them to be used.
Click Discover and select whether to run the discovery now or schedule the discovery for a later time.
- To run the discovery now, click the Now radio button and click Start .
- To schedule the discovery for a later time, click the Later radio button, define the date and time, and click Start .
Click the notifications icon to view the scheduled discovery tasks. Click Edit to edit the discovery task before the discovery starts. Click Cancel to cancel the scheduled discovery job before it starts.
The Discoveries window displays the results of your scan.
The Discovery Details pane shows the status (active or inactive) and the Discovery configuration. The Discovery Devices pane displays the host names, IP addresses, and status of the discovered devices.
Discover Your Network Using an IP Address Range
You can discover devices using an IP address range, CDP, or LLDP. This procedure shows you how to discover devices and hosts using an IP address range. For more information about the other Discovery methods, see Discover Your Network Using CDP and Discover Your Network Using LLDP.
Before you begin
Your devices must have the required device configurations, as described in Discovery Prerequisites.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click Add Discovery .
In the Discovery Name field, enter a name.
Expand the IP Address/Ranges area, if it is not already visible, and configure the following fields:
- For Discovery Type , click IP Address/Range .
- In the From and To fields, enter the beginning and ending IP addresses (IP address range) for Cisco DNA Center to scan, and click + . You can enter a single IP address range or multiple IP addresses for the discovery scan.
Note Cisco Wireless Controllers must be discovered using the management IP address instead of the service port IP address. If not, the related wireless controller 360 and AP 360 pages will not display any data. - None : Allows the device to use any of its IP addresses.
- Use Loopback IP : Specify the device's loopback interface IP address.
Note If you choose Use Loopback IP and the device does not have a loopback interface, Cisco DNA Center chooses a management IP address using the logic described in Preferred Management IP Address. Expand the Credentials area and configure the credentials that you want to use for the Discovery job.
Choose any of the global credentials that have already been created or configure your own Discovery credentials. If you configure your own credentials, you can save them for only the current job by clicking Save , or you can save them for the current and future jobs by checking the Save as global settings check box and then clicking Save .
- Make sure that the global credentials that you want to use are selected. If you do not want to use a credential, deselect it.
- To add additional credentials, click Add Credentials .
- To configure CLI credentials, configure the following fields:
Table 6. CLI Credentials
Field Description Name/Description Name or phrase that describes the CLI credentials. Username Name that is used to log in to the CLI of the devices in your network. Password Password that is used to log in to the CLI of the devices in your network. For security reasons, re-enter the password as confirmation. Note Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration. Note Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration. Click SNMP v2c and configure the following fields:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the SNMPv2c settings that you are adding.
- Read Community : Read-only community string password used only to view SNMP information on the device.
Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Name/Description : Name or description of the SNMPv2c settings that you are adding.
- Write Community : Write community string used to make changes to the SNMP information on the device.
Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Authentication type to be used. (Enabled if you select AuthPriv or AuthNoPriv as the authentication mode.) Choose one of the following authentication types:
- SHA : Authentication based on HMAC-SHA.
- MD5 : Authentication based on HMAC-MD5.
SNMPv3 password used for gaining access to information from devices that use SNMPv3. These passwords (or passphrases) must be at least eight characters in length.
- Some wireless controllers require that passwords (or passphrases) be at least 12 characters long. Be sure to check the minimum password requirements for your wireless controllers. Failure to ensure these required minimum character lengths for passwords results in devices not being discovered, monitored, or managed by Cisco DNA Center .
- Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Privacy type. (Enabled if you select AuthPriv as the authentication mode.) Choose one of the following privacy types:
- AES128 : CBC mode AES for encryption.
- None : No privacy.
SNMPv3 privacy password that is used to generate the secret key for encrypting messages that are exchanged with devices that support AES128 encryption. Passwords (or passphrases) must be at least eight characters long.
- Some wireless controllers require that passwords (or passphrases) be at least 12 characters long. Be sure to check the minimum password requirements for your wireless controllers. Failure to ensure these required minimum character lengths for passwords results in devices not being discovered, monitored, or managed by Cisco DNA Center .
- Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Table 9. SNMP Properties
Field Description Retries Number of times Cisco DNA Center tries to communicate with network devices using SNMP. Timeout Number of seconds between retries. (Optional) Click HTTP(S) and configure the following fields:
Specifies the kind of HTTPS credentials you are configuring. Valid types are Read or Write .
You can configure up to 10 HTTPS read credentials:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the HTTPS credentials that you are adding.
- Username : Name used to authenticate the HTTPS connection.
- Password : Password used to authenticate the HTTPS connection. Passwords are encrypted for security and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Port : Number of the TCP/UDP port used for HTTPS traffic. The default is port number 443 (the well-known port for HTTPS).
The password must contain from 7 to 128 characters, including at least one:
- Lowercase letter (a - z)
- Uppercase letter (A - Z)
- Number (0 - 9)
- Special character: # _ * ? –
The password cannot contain spaces or angle brackets (< >). Note that some Cisco IOS XE devices do not allow a question mark (?).
You can configure up to 10 HTTPS write credentials:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the HTTPS credentials that you are adding.
- Username : Name used to authenticate the HTTPS connection.
- Password : Password used to authenticate the HTTPS connection. Passwords are encrypted for security and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Port : Number of the TCP/UDP port used for HTTPS traffic. The default is port number 443 (the well-known port for HTTPS).
The password must contain from 7 to 128 characters, including at least one:
- Lowercase letter (a - z)
- Uppercase letter (A - Z)
- Number (0 - 9)
- Special character: # _ * ? –
The password cannot contain spaces or angle brackets (< >). Note that some Cisco IOS XE devices do not allow a question mark (?).
- 830 (the default port number)
- Any other port that is available on the device
- A custom port that Cisco DNA Center configures (if Device Controllability is enabled)
NETCONF provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete configurations of network devices. NETCONF will be disabled if you choose Telnet in the Advanced area.
(Optional) To configure the protocols that are to be used to connect with devices, expand the Advanced area and do the following tasks:
- Click the protocols that you want to use. A green check mark indicates that the protocol is selected. Valid protocols are SSH (default) and Telnet .
- Drag and drop the protocols in the order that you want them to be used.
Click Discover and select whether to run the discovery now or schedule the discovery for a later time.
- To run the discovery now, click the Now radio button and click Start .
- To schedule the discovery for a later time, click the Later radio button, define the date and time, and click Start .
Click the notifications icon to view the scheduled discovery tasks. Click Edit to edit the discovery task before the discovery starts. Click Cancel if you want to cancel the scheduled discovery job before it starts.
The Discoveries window displays the results of your scan.
The Discovery Details pane shows the status (active or inactive) and the Discovery configuration. The Discovery Devices pane displays the host names, IP addresses, and status of the discovered devices.
Discover Your Network Using LLDP
You can discover devices using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), CDP, or an IP address range. This procedure shows you how to discover devices and hosts using LLDP. For more information about the other discovery methods, see Discover Your Network Using CDP and Discover Your Network Using an IP Address Range.
- The Discovery function requires the correct SNMP Read Only (RO) community string. If an SNMP RO community string is not provided, as a best effort, the Discovery function uses the default SNMP RO community string, public.
- CLI credentials are not required to discover hosts; hosts are discovered through the network devices to which they are connected.
Before you begin
- Enable LLDP on your network devices.
- Configure your network devices, as described in Discovery Prerequisites.
- Configure your network device's host IP address as the client IP address. (A host is an end-user device, such as a laptop computer or mobile device.)
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click Add Discovery .
In the Discovery Name field, enter a name.
Expand the IP Address/Range area and configure the following fields:
- For Discovery Type , click LLDP .
- In the IP Address field, enter a seed IP address for Cisco DNA Center to start the Discovery scan.
- (Optional) In the Subnet Filter field, enter an IP address or subnet to exclude from the Discovery scan. You can enter addresses either as an individual IP address ( x.x.x.x ) or as a classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) address ( x.x.x.x/y ) , where x.x.x.x refers to the IP address and y refers to the subnet mask. The subnet mask can be a value from 0 to 32.
- Click + . Repeat Step c and Step d to exclude multiple subnets from the Discovery job.
- (Optional) In the LLDP Level field, enter the number of hops from the seed device that you want to scan. Valid values are from 1 to 16. The default value is 16. For example, LLDP level 3 means that LLDP will scan up to three hops from the seed device.
- For Preferred Management IP , choose one of the following options:
- None : Allows the device use any of its IP addresses.
- Use Loopback IP : Specify the device's loopback interface IP address.
Note If you choose this option and the device does not have a loopback interface, Cisco DNA Center chooses a management IP address using the logic described in Preferred Management IP Address. Note To use the loopback interface IP address as the preferred management IP address, make sure that the LLDP neighbor's IP address is reachable from Cisco DNA Center . Expand the Credentials area and configure the credentials that you want to use for the Discovery job.
Choose any of the global credentials that have already been created, or configure your own Discovery credentials. If you configure the credentials, you can choose to save them for future jobs by checking the Save as global settings check box.
- Make sure that the global credentials that you want to use are selected. If you do not want to use a credential, deselect it.
- To add additional credentials, click Add Credentials .
- For CLI credentials, configure the following fields:
Table 11. CLI Credentials
Field Description Name/Description Name or phrase that describes the CLI credentials. Username Name that is used to log in to the CLI of the devices in your network. Password Password that is used to log in to the CLI of the devices in your network. For security reasons, re-enter the password as confirmation. Note Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration. Note Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration. Click SNMP v2c and configure the following fields:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the SNMPv2c settings that you are adding.
- Read Community : Read-only community string password used only to view SNMP information on the device.
Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Name/Description : Name or description of the SNMPv2c settings that you are adding.
- Write Community : Write community string used to make changes to the SNMP information on the device.
Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Authentication type to be used. (Enabled if you select AuthPriv or AuthNoPriv as the authentication mode.) Choose one of the following authentication types:
- SHA : Authentication based on HMAC-SHA.
- MD5 : Authentication based on HMAC-MD5.
SNMPv3 password used for gaining access to information from devices that use SNMPv3. These passwords (or passphrases) must be at least eight characters in length.
- Some wireless controllers require that passwords (or passphrases) be at least 12 characters long. Be sure to check the minimum password requirements for your wireless controllers. Failure to ensure these required minimum character lengths for passwords results in devices not being discovered, monitored, or managed by Cisco DNA Center .
- Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Privacy type. (Enabled if you select AuthPriv as the authentication mode.) Choose one of the following privacy types:
- AES128 : CBC mode AES for encryption.
- None : No privacy.
SNMPv3 privacy password that is used to generate the secret key for encrypting messages that are exchanged with devices that support AES128 encryption. Passwords (or passphrases) must be at least eight characters long.
- Some wireless controllers require that passwords (or passphrases) be at least 12 characters long. Be sure to check the minimum password requirements for your wireless controllers. Failure to ensure these required minimum character lengths for passwords results in devices not being discovered, monitored, or managed by Cisco DNA Center .
- Passwords are encrypted for security reasons and are not displayed in the configuration.
Table 14. SNMP Properties
Field Description Retries Number of times Cisco DNA Center tries to communicate with network devices using SNMP. Timeout Number of seconds between retries. (Optional) Click HTTP(S) and configure the following fields:
Specifies the kind of HTTPS credentials you are configuring. Valid types are Read or Write .
You can configure up to 10 HTTPS read credentials:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the HTTPS credentials that you are adding.
- Username : Name used to authenticate the HTTPS connection.
- Password : Password used to authenticate the HTTPS connection. Passwords are encrypted for security and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Port : Number of the TCP/UDP port used for HTTPS traffic. The default is port number 443 (the well-known port for HTTPS).
The password must contain from 7 to 128 characters, including at least one:
- Lowercase letter (a - z)
- Uppercase letter (A - Z)
- Number (0 - 9)
- Special character: # _ * ? –
The password cannot contain spaces or angle brackets (< >). Note that some Cisco IOS XE devices do not allow a question mark (?).
You can configure up to 10 HTTPS write credentials:
- Name/Description : Name or description of the HTTPS credentials that you are adding.
- Username : Name used to authenticate the HTTPS connection.
- Password : Password used to authenticate the HTTPS connection. Passwords are encrypted for security and are not displayed in the configuration.
- Port : Number of the TCP/UDP port used for HTTPS traffic. The default is port number 443 (the well-known port for HTTPS).
The password must contain from 7 to 128 characters, including at least one:
- Lowercase letter (a - z)
- Uppercase letter (A - Z)
- Number (0 - 9)
- Special character: # _ * ? –
The password cannot contain spaces or angle brackets (< >). Note that some Cisco IOS XE devices do not allow a question mark (?).
(Optional) To configure the protocols to be used to connect with devices, expand the Advanced area and do the following tasks:
- Click the names of the protocols that you want to use. A green check mark indicates that the protocol is selected. Valid protocols are SSH (default) and Telnet .
- Drag and drop the protocols in the order that you want them to be used.
Click Discover and select whether to run the discovery now or schedule the discovery for a later time.
- To run the discovery now, click the Now radio button and click Start .
- To schedule the discovery for a later time, click the Later radio button, define the date and time, and click Start .
Click the notifications icon to view the scheduled discovery tasks. Click Edit to edit the discovery task before the discovery starts. Click Cancel if you want to cancel the scheduled discovery job before it starts.
The Discoveries window displays the results of your scan.
The Discovery Details pane shows the status (active or inactive) and the Discovery configuration. The Discovery Devices pane displays the host names, IP addresses, and status of the discovered devices.
Manage Discovery Jobs
Stop and Start a Discovery Job
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click View All Discoveries .
To stop an active Discovery job, perform these steps:
- From the Discoveries pane, select the corresponding job.
- Click Stop .
To restart an inactive Discovery job, perform these steps:
- From the Discoveries pane, select the corresponding job.
- Click Re-discover to restart the selected job.
Clone a Discovery Job
You can clone a Discovery job and retain all of the information defined for that job.
Before you begin
You should have run at least one Discovery job.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click View All Discoveries .
From the Discoveries pane, select the Discovery job.
Click Copy & Edit .
Cisco DNA Center creates a copy of the Discovery job, named Copy of Discovery_Job .
(Optional) Change the name of the Discovery job.
Define or update the parameters for the new Discovery job.
Delete a Discovery Job
You can delete a Discovery job whether it is active or inactive.Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click View All Discoveries .
From the Discoveries pane, select the Discovery job that you want to delete.
Click OK to confirm.
View Discovery Job Information
You can view information about a Discovery job, such as the settings and credentials that were used. You also can view the historical information about each Discovery job that was run, including information about the specific devices that were discovered or that failed to be discovered.
Before you begin
Run at least one Discovery job.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Tools > Discovery .
Click View All Discoveries .
From the Discoveries pane, select the Discovery job. Alternatively, use the Search function to find a Discovery job by device IP address or name.
Click the down arrow next to one of the following areas for more information:
- Discovery Details : Displays the parameters that were used to run the Discovery job. Parameters include attributes such as the CDP or LLDP level, IP address range, and protocol order.
- Credentials : Provides the names of the credentials that were used.
- History : Lists each Discovery job that was run, including the time when the job started, and whether any devices were discovered. To successfully discover embedded wireless controllers, the NETCONF port must be configured. If the NETCONF port is not configured, wireless data is not collected. Use the Filter function to display devices by any combination of IP addresses or ICMP, CLI, HTTPS, or NETCONF values.
Design Network Hierarchy
You can create a network hierarchy that represents your network's geographical locations. Your network hierarchy can contain sites, which contains buildings and areas.
Design a New Network Infrastructure
The Design area is where you create the structure and framework of your network, including the physical topology, network settings, and device type profiles that you can apply to devices throughout your network. Use the Design workflow if you do not already have an existing infrastructure. If you have an existing infrastructure, use the Discovery feature. For more information, see About Discovery.
You can perform these tasks in the Design area:
Procedure
Create your network hierarchy.
Define global network settings.
Define network profiles.
About Network Hierarchy
You can create a network hierarchy that represents your network's geographical locations. Your network hierarchy can contain sites, which in turn contain buildings and areas. You can create site and building IDs to easily identify where to apply design settings or configurations later. By default, there is one site called Global .
The network hierarchy has a predetermined hierarchy:
- Areas or Sites do not have a physical address, such as the United States. You can think of areas as the largest element. Areas can contain buildings and subareas. For example, an area called United States can contain a subarea called California, and the subarea California can contain a subarea called San Jose.
- Buildings have a physical address and contain floors and floor plans. When you create a building, you must specify a physical address and latitude and longitude coordinates. Buildings cannot contain areas. By creating buildings, you can apply settings to a specific area.
- Floors are within buildings and consist of cubicles, walled offices, wiring closets, and so on. You can add floors only to buildings.
You can change the site hierarchy for unprovisioned devices while preserving AP locations on sitemaps. Note, however, that you cannot move an existing floor to a different building.
The following is a list of tasks that you can perform:
- Create a new network hierarchy. For more information, see Create a Site in a Network Hierarchy.
- Upload an existing network hierarchy from Cisco Prime Infrastructure. For more information, see Upload an Existing Site Hierarchy.
Guidelines for Image Files to Use in Maps
- Use a graphical application that can save the map image files to any of these formats: .jpg, .gif, .png, .pdf, .dxf, and .dwg.
- Ensure that the dimension of an image is larger than the combined dimension of all the buildings and outside areas that you plan to add to the campus map.
- Map image files can be of any size. Cisco DNA Center imports the original image to its database at a full definition, but during display, it automatically resizes them to fit the workspace.
- Obtain the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the site in feet or meters before importing. This helps you to specify these dimensions during map import.
Create a Site in a Network Hierarchy
Cisco DNA Center allows you to easily define physical sites and then specify common resources for those sites. The Design area uses a hierarchical format for intuitive use, while eliminating the need to redefine the same resource in multiple places when provisioning devices. By default, there is one site called Global . You can add more sites, buildings, and areas to your network hierarchy. You must create at least one site before you can use the provision features.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
Result: A world map appears in the right pane.
From the map toolbar, click + Add Site and choose Add Area .

You can also hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the parent site in the left pane, and then choose Add Area .
Enter the site name in the Area Name field.
The Area Name field has the following restrictions:
From the Parent drop-down list, choose a parent node.
By default, Global is the parent node.
Result: The site is created under the parent node in the left pane.
Add a Building
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the Network Hierarchy window, click +Add Site > Add Building .

Alternatively, you can hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the parent site in the left pane, and choose Add Building .
Add the building details in the Add Building pop-up:
-
In the Building Name field, enter a name for the building.
Note By default, Global is the parent node. Note Alternatively, you can click on the map to input the address. Adding an address causes the Longitude and Latitude coordinates fields to be automatically populated. You can manually change the longitude and latitude coordinates to change the address. Result: The building is created and appears under the parent site in the left pane.
Add a Floor to a Building
After you add a building, you will need to create floors for it.
Procedure

Click the Menu icon and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .

In the left pane, hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the building of the floor and choose Add Floor .
In the Floor Name field, enter a name for the floor.
The Floor Name field has the following restrictions:
For the Type (RF Model) drop-down list, choose the RF model to apply for the floor.
The RF model determines how the RF is calculated based on the characteristics of the floor.
In the Floor Image area, drag and drop the floor plan file to upload the floor plan.
Cisco DNA Center supports the file types DXF, DWG, JPG, GIF, PNG, and PDF for floor plans.

After you import a floor plan, make sure that you enable the overlay visibility (From the floor, click View Options and enable the overlay toggles in Overlay Objects ). By default, overlays are not displayed after you import a map.
If you upload a CAD file (DXF or DWG file type), use the Floormap pop-up to choose the CAD layers that you want to appear as floor elements in the map:
- For the 2D column, check the check boxes of the CAD layer that you want to appear in the 2D view.
- For the 3D Wall/Shelving Type column, use the drop-down list for a CAD layer to specify the type for the wall or shelving.
Note For a layer to appear in the 3D view, it is required to have a 3D Wall/Shelving Type value. The wall/shelving type affects attenuation and how the heatmap is calculated. Enter the floor map dimensions in the Width , Length , and Height fields.
Manage Network Hierarchy
Upload an Existing Site Hierarchy
You can upload a CSV file or a map archive file that contains an existing network hierarchy. For example, you can upload a CSV file with location information that you exported from Cisco Prime Infrastructure. For information about exporting maps from Cisco Prime Infrastructure, see Export Maps Archive.
Before importing a map archive file into Cisco DNA Center , make sure that the devices such as Cisco Wireless Controllers and the associated APs are discovered and listed on the Cisco DNA Center inventory page.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
From the tool bar, click Import and choose Import Sites .
Drag and drop your CSV file, or navigate to where your CSV file is located, then click Import .
If you do not have an existing CSV file, click Download Template to download a CSV file that you can edit and upload.
To import the Cisco Prime Infrastructure maps tar.gz archive file, choose Import > Map Import .
Drag and drop the map archive file into the boxed area in the Import Site Hierarchy Archive dialog box.
Click Save to upload the file.
Result: The Import Preview window appears, which shows the imported file.
Export Maps Archive
You can export maps archive files from Cisco Prime Infrastructure and import them into Cisco DNA Center .
Procedure
From the Cisco Prime Infrastructure user interface, choose Maps > Wireless Maps > Site Maps (New) .
From the Export drop-down list, choose Map Archive .
On the Select Sites window, configure the following. You can either select map information or calibration information to be included in the maps archive.
- Map Information : Click the On or Off button to include map information in the archive.
- Calibration Information : To export calibration information, click the On or Off button. Click the Calibration Information for selected maps or the All Calibration Information radio button. If you select Calibration Information for selected maps , the calibration information for the selected site maps is exported. If you select All Calibration Information , the calibration information for the selected map, along with additional calibration information that is available in the system, is also exported.
- In the Sites left pane, check one or more check boxes of the site, campus, building floor, or outdoor area that you want to export. Check the Select All check box to export all the maps.
Click Generate Map Archive . A message Exporting data is in progress is displayed.
Result: A tar file is created and is saved to your local machine.
Search the Network Hierarchy
You can search the network hierarchy to quickly find a site, building, or area. This is particularly helpful after you have added many sites, areas, or buildings.
Procedure
To search the tree hierarchy, in the Find Hierarchy search field in the left pane and enter either the partial or full name of the site, building, or floor name that you are searching.
Result: The tree hierarchy is filtered based on the text you enter in the search field.
Edit a Site
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .

In the left pane, hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the site and choose Edit Area .
In the Edit Area pop-up, make the necessary edits.
Click Update to save your changes.
Delete a Site
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .

In the left pane, hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the site and choose Delete Area .
In the dialog box, click OK to confirm the deletion.
Edit a Building
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .

In the left pane, hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the building and choose Edit Building .
In the Edit Building pop-up, make the necessary edits.
Click Update to save your changes.
Delete a Building
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .

In the left pane, hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the building and choose Delete Building .
In the dialog box, click OK to confirm the deletion.
Deleting a building deletes all its container maps. APs from the deleted maps are moved to Unassigned state.
Edit a Floor
After you add a floor, you can edit the floor map so that it contains obstacles, areas, and APs on the floor.
Procedure

Click the Menu icon and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .

In the left pane, hover your cursor over the ellipsis next to the floor and choose Edit Floor .
In the Edit Floor pop-up, make the necessary changes.
Click Update to save the changes.
Monitor a Floor Map in 2D
The floor view navigation pane provides access to multiple map functions like:
- Use the Find feature located at the top-right corner of the floor map window to find specific floor elements such as APs, sensors, clients, and so on. The elements that match the search criteria are displayed on the floor map along with a table in the right pane. When you hover your mouse over the table, it points to the search element on the floor map with a connecting line.
- Click the
 icon at the top-right corner of the floor map window to:
icon at the top-right corner of the floor map window to: - Export a floor plan as a PDF.
- Measure the distance on the floor map.
- Set the scale to modify the floor dimensions.
- Click the
 icon at the bottom-right of the floor map window to zoom in on a location. The zooming levels depend upon the resolution of an image. A high-resolution image might provide more zoom levels. Each zoom level comprises of a different style map shown at different scales, each one showing the corresponding details. Some maps are of the same style, but at a smaller or larger scale.
icon at the bottom-right of the floor map window to zoom in on a location. The zooming levels depend upon the resolution of an image. A high-resolution image might provide more zoom levels. Each zoom level comprises of a different style map shown at different scales, each one showing the corresponding details. Some maps are of the same style, but at a smaller or larger scale. - Click the
 icon to see a map with fewer details.
icon to see a map with fewer details. - Click the
 icon to view the map icon legend.
icon to view the map icon legend.
Edit Floor Map Elements and Overlays
While viewing a floor map, click Add/Edit from the map toolbar to enter edit mode. While in edit mode, you can do the following:
Add, position, and delete the following devices:
Add, edit, and delete the following overlay objects:
Guidelines for Placing Access Points
Follow these guidelines while placing APs on the floor map:
- Place APs along the periphery of coverage areas to keep devices close to the exterior of rooms and buildings. APs placed in the center of these coverage areas provide good data on devices that would otherwise appear equidistant from all other APs.
- Location accuracy can be improved by increasing overall AP density and moving APs close to the perimeter of the coverage area.
- In long and narrow coverage areas, avoid placing APs in a straight line. Stagger them so that each AP is more likely to provide a unique snapshot of the device location.
- Although the design provides enough AP density for high-bandwidth applications, location suffers because each AP view of a single device is not varied enough. Therefore, location is difficult to determine. Move the APs to the perimeter of the coverage area and stagger them. Each has a greater likelihood of offering a distinctly different view of the device, resulting in higher location accuracy.
- For optimal heatmap visibility on floor maps, configure the AP height to approximately 10 feet (3 meters) or lower.
Add, Position, and Delete APs
Cisco DNA Center computes heatmaps for the entire map that show the relative intensity of the Radio Frequency (RF) signals in the coverage area. For 2D wireless maps, the heatmap is only an approximation of the actual RF signal intensity because it does not consider the RF signal reflection and other effects impacting the signal.
Before you begin
Make sure that you have Cisco APs in your inventory. If not, discover APs using the Discovery feature. See About Discovery.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, click the building floor.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
Ensure the APs toggle is enabled from the map toolbar.
From the map left pane, click Add APs .
From the Add APs slide-in pane, check the check boxes of the access points to select the APs in bulk, and click Add Selected . Alternatively click Add next to an access point.
You can search for access points using the search option available. Use the Filter field to search for access points using the AP name, MAC address, model, or Cisco Wireless Controller. The search is case-insensitive. The search result appear in a table. Click Add to add one or more of these APs to the floor area.
Result: Newly added APs appear in the Unpositioned category from the map left pane in edit mode.
Close the Add APs window after assigning APs to the floor area.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map left pane, click an AP from the Unpositioned category to position the AP.
To position the AP, do one of the following:
- Click on the location of the floor map to position the AP.
- From the Edit AP slide-in pane, enter the x and y coordinates in the corresponding fields.
- You can draw three points on the floor map and position the AP by using the selected points. To do this:
- From the Edit AP slide-in pane, click Position by 3 points .
- To define the points, click anywhere on the floor map to start drawing the first point. Click again to finish drawing a point. A dialog box appears to set the distance to first point. Enter the distance, in meters, and click Set Distance .
- Define the second and third points similarly, and click Save .
- You can define two walls on the floor map and position APs between the defined walls. This helps you to know the position of APs between the two walls. This helps you to understand the AP position between the walls.
- From the Edit AP slide-in pane, click Position by 2 walls .
- To define the first wall, click anywhere on the floor map to start drawing the line. Click again to finish drawing a line. A dialog box appears to set the distance to the first wall. Enter the distance in meters and click Set Distance .
- Define the second wall similarly and click Save . Result: The AP is placed automatically based on the defined distance between the walls.
Use the Edit AP slide-in pane to configure details of the AP such as:
- AP Name : Shows the AP name.
- MAC Address : Displays the MAC address.
- AP Model : Indicates the AP model of the selected access point.
- x : Indicates the x-axis coordinate of the AP. You can manually enter the value.
- y : Indicates the y-axis coordinate of the AP. You can manually enter the value.
- AP Height : Indicates the height of the access point. You can manually enter the value.
- Antenna : Antenna type for this access point.
Note For external APs, you must select an antenna, or the AP will not be present in the map. Note This option does not appear for omnidirectional antennas because their pattern is nondirectional in azimuth. After you have completed placing and configuring access points, click Save from the map toolbar.
If a Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences (CMX) is synchronized with Cisco DNA Center , you can view the location of clients on the heatmap. See Create Cisco CMX Settings.
Result: The heatmap is generated based on the new position of the AP.
To delete APs from the floor map, click Remove APs from the map left pane while in edit mode.
From the Delete APs slide-in pane, check the check boxes next to the access points that you want to delete, and click Delete Selected .
- To delete all the access points, click Select All and then Delete Selected .
- To delete an access point from the floor, click the Delete icon.
- Use Quick Filter and search using the AP name, MAC address, model, or controller. The search is case-insensitive. The search result appears in the table. Click the Delete icon to delete the APs from the floor area.
Quick View of APs
Hover your cursor over the AP icon on the floor map to view AP details, Rx neighbor information, client information, and Device 360 information.
- Click Info to view the following AP details:
- Associated : Indicates whether an AP is associated or not.
- Name : AP name.
- MAC Address : MAC address of the AP.
- Model : AP model number.
- Admin/Mode : Administration status of the AP mode.
- Type : Radio type.
- OP/Admin : Operational status and AP mode.
- Channel : Channel number of the AP.
- Antenna : Antenna name.
- Azimuth : Direction of the antenna.
NoteFor Device 360 to open, you must have the Assurance application installed. Add, Position, and Delete Sensors
Make sure you have the Cisco AP 1800S sensor in your inventory. The Cisco Aironet 1800s Active Sensor must be provisioned using Plug and Play for it to show up in the Inventory. See the Provision the Wireless Cisco Aironet 1800s Active Sensor topic in the Cisco DNA Assurance User Guide.
A sensor device is a dedicated AP 1800s sensor. The Cisco Aironet 1800s Active Sensor gets bootstrapped using PnP. After it obtains the Assurance server reachability details, it directly communicates with the Assurance server.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, click the building floor.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map toolbar, click the Sensors toggle.
From the Add Sensors slide-in pane, check the check boxes of the sensors that you want to add. Alternatively, click Add next to the sensor row to add sensors.
You can search for specific sensors using the search option. Use the Filter field and search using the name, MAC address, or model of a sensor. The search is case-insensitive. The search results are displayed in the table. Click Add to add one or more these sensors to the floor area.
Result: Newly added sensors appear in the Unpositioned category from the map left pane in edit mode.
Close the Add Sensors slide-in pane after assigning sensors to the floor map.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map left pane, click a sensor in the Unpositioned category to position the sensor.
Click on the location of the floor map to position the sensor.
- You can use the x , y , and sensorHeight fields in the Sensor Details slide-in pane to enter the exact x, y, and z coordinates for the sensor.
After you have completed placing and adjusting sensors, click Save .
To delete a sensor from the floor map, click Remove APs from the map left pane while in edit mode.
Check the check boxes of the sensors that you want to delete, and click Delete Selected .
- To delete all the sensors, click Select All , and click Delete Selected .
- To delete a sensor from the floor, click the Delete icon next to that sensor.
- Use Quick Filter and search using the name, MAC address, or model. The search is case-insensitive. The search results are displayed in a table. Click the Delete icon to delete one or more sensors from the floor area.
Add Coverage Areas
By default, any floor area or outside area defined as part of a building map is considered as a wireless coverage area.
If you have a building that is nonrectangular or you want to mark a nonrectangular area within a floor, you can use the map editor to draw a coverage area or a polygon-shaped area.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, click the building floor.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map toolbar, click the Coverage Areas toggle.
From the map left pane, click the Coverage Area icon.
In the Coverage Area pop-up window, enter a name for the coverage area in the field and click Add Coverage .
Use the drawing tool to create the coverage area shape:
-
Click on the map to create a point and continue creating points to define the coverage area shape.
Note The coverage area shape must have at least 3 points. After you can finish creating the coverage area, click Save from the map toolbar.
To edit a coverage area, do the following:
- From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
- From the map toolbar, click the Coverage Areas toggle.
- You can click and drag the points of the coverage area to redefine the shape.
- To edit the coverage area name, right-click a coverage area and choose Edit .
- After finishing making edits, click Save from the map toolbar.
To delete a coverage area, do the following:
- From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
- From the map toolbar, click the Coverage Areas toggle.
- Right-click the coverage area and choose Delete .
- After finishing deleting, click Save from the map toolbar.
Create Obstacles
You can create obstacles so that they can be considered while computing Radio Frequency (RF) prediction heatmaps for access points.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, select the floor.
Click Edit , which is located above the floor plan in the middle pane.
In the Overlays panel, next to Obstacles , click Add .
In the Obstacle Creation dialog box, choose an obstacle type from the Obstacle Type drop-down list. The type of obstacles that you can create are Thick Wall , Light Wall , Heavy Door , Light Door , Cubicle , and Glass .
Click Add Obstacle .
Move the drawing tool to the area where you want to create an obstacle.
Click the drawing tool to start and stop a line.
After you have outlined the area, double-click the area to highlight it.
In the Obstacle Creation window, click Done .
Click Save to save the obstacle on the floor map.
To edit an obstacle, in the Overlays panel, next to Obstacles , click Edit .
All the available obstacles are highlighted on the map.
Click Save after the changes.
To delete an obstacle, in the Overlays panel, next to Obstacles , click Delete .
All the available obstacles are highlighted on the map.
Hover your cursor over the obstacle and click to delete.
Location Region Creation
You can create inclusion and exclusion areas to further refine location calculations on a floor. You can define the areas that are included (inclusion areas) in the calculations and those areas that are not included (exclusion areas). For example, you might want to exclude areas such as an atrium or stairwell within a building, but include a work area, such as cubicles, labs, or manufacturing floors.
Guidelines for Placing Inclusion and Exclusion Areas on a Floor Map
- Inclusion and exclusion areas can be any polygon-shaped area and must have at least 3 points.
- You can only define 1 inclusion region on a floor. By default, an inclusion region is defined for each floor area when it is created. The inclusion region is indicated by a solid aqua line, and generally outlines the entire floor area.
- You can define multiple exclusion regions on a floor area.
Define an Inclusion Region on a Floor
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, click a building floor.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map toolbar, click the Location Regions toggle.
From the map left pane, click the Inclusion icon.
Use the drawing tool to create the inclusion area:
- Click on the map to create point and continue creating points until you have created the shape for the inclusion area.
- To finalize the shape, click the Inclusion icon from the left pane to exit drawing mode. Alternatively, you can double-click on the map to finalize the shape. If you want to cancel the shape, right-click on the map.
- To move an existing inclusion area, drag and drop the shape to the new location.
- To remove an existing inclusion area, right-click the shape and choose Delete .
After you are finish creating inclusion areas, click Save from the map toolbar.
Define an Exclusion Region on a Floor
To further refine location calculations on a floor, you can define areas that are excluded (exclusion areas) in the calculations. For example, you might want to exclude areas such as an atrium or stairwell within a building. As a rule, exclusion areas are defined within the borders of an inclusion area.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, click a building floor.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map toolbar, click the Location Regions toggle.
From the map left pane, click the Exclusion icon.
Use the drawing tool to create the exclusion area:
- Click on the map to create point and continue creating points until you have created the shape for the exclusion area.
- To finalize the shape, click the Exclusion icon from the left pane to exit drawing mode. Alternatively, you can double-click on the map to finalize the shape. If you want to cancel the shape, right-click on the map.
- To move an existing exclusion area, drag and drop the shape to the new location.
- To remove an existing exclusion area, right-click the shape and choose Delete .
After you are finish creating exclusion areas, click Save from the map toolbar.
Edit Location Regions
Procedure
In the Overlays panel, next to Location Regions , click Edit .
Make the necessary changes, and click Save .
Delete Location Regions
Procedure
In the Overlays panel, next to Location Regions , click Delete .
Hover your cursor over the region that you want to delete, and click Delete .
Create a Rail
You can define a rail line on a floor that represents a conveyor belt. Also, you can define an area around the rail area known as the snap-width to further assist location calculations. This represents the area in which you expect clients to appear. Any client located within the snap-width area is plotted on the rail line (majority) or outside of the snap-width area (minority).
The snap-width area is defined in feet or meters (user-defined) and represents the distance that is monitored on either side (east and west or north and south) of the rail.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, select the floor.
Click Edit , which is located above the floor plan in the middle pane.
In the Overlays panel, next to Rails , click Add .
Enter a snap-width (feet or meters) for the rail, and click Add Rail .
A drawing icon appears.
Click the drawing icon at the starting point of the rail line. Click again when you want to stop drawing the line or change the direction of the line.
Click the drawing icon twice when the rail line is drawn on the floor map. The rail line appears on the map and is bordered on either side by the defined snap-width region.
In the Overlays panel, next to Rails , click Edit .
The available rails are highlighted on the map.
Make changes, and click Save .
In the Overlays panel, next to Rails , click Delete .
All the available rail lines are highlighted on the map.
Hover your cursor over the rail line that you want to delete, and click Delete .
Place Markers
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Hierarchy .
In the left pane, click a building floor.
From the map toolbar, click Add/Edit .
From the map toolbar, click the Markers toggle.
Enter the name for the marker, and then click Add Marker .
Use the drawing tool to place the marker:
- Click on the map to place the marker.
- To move the marker,
- To edit an existing marker, right-click the marker and choose Edit .
- To remove an existing marker, right-click the marker and choose Delete .
Click Save from the map toolbar.
Floor View Options
Click the View Options, which is located above the floor plan in the middle pane. The floor map along with these panels appear in the right pane: Access Points , Sensor , Overlay Objects , Map Properties , and Global Map Properties .
You can modify the appearance of the floor map by selecting or unselecting various parameters. For example, if you want to view only the access point information on the floor map, check the Access Point check box. You can expand each panel to configure various settings available for each floor element.
View Options for Access Points
To view access points on a map, click the On/Off button next to Access Points . Expand the Access Points panel to configure these settings:
- Display Label : From the drop-down list, choose a text label that you want to view on the floor map for the AP. The available display labels are:
- None : No labels are displayed for the selected access point.
- Name : AP name.
- AP MAC Address : AP MAC address.
- Controller IP : IP address of Cisco Wireless Controller to which the access point is connected.
- Radio MAC Address : Radio MAC address.
- IP Address
- Channel: Cisco Radio channel number or Unavailable (if the access point is not connected).
- Coverage Holes: Percentage of clients whose signal has become weaker until the client lost its connection. It shows Unavailable for access points that are not connected and MonitorOnly for access points that are in monitor-only mode.
- TX Power : Current Cisco Radio transmit power level (with 1 being high) or Unavailable (if the access point is not connected). If you change the radio band, the information on the map changes accordingly. The power levels differ depending on the type of access point. The Cisco Aironet 1000 Series Lightweight Access Point accepts a value between 1 and 5 ; the Cisco Aironet 1230AG Series Access Point accepts a value between 1 and 7 ; and the Cisco Aironet 1240AG Series Access Point and Cisco Aironet 1100 Series Access Point accept a value between 1 and 8 .
- Channel and Tx Power : Channel and transmit power level (or Unavailable if the access point is not connected).
- Utilization : Percentage of bandwidth used by the associated client devices (including receiving, transmitting, and channel utilization). Displays Unavailable for disassociated access points and MonitorOnly for access points in monitor-only mode.
- Tx Utilization : Transmitted (Tx) utilization for the specified interface.
- Rx Utilization : Received (Rx) utilization for the specified interface.
- Ch Utilization : Channel utilization for the specified access point.
- Assoc. Clients : Total number of clients associated.
- Dual-Band Radios : Identifies and marks the XOR dual-band radios on the Cisco Aironet 2800 and 3800 Series Access Points.
- Health Score : AP health score.
- Issue Count
- Coverage Issues
- AP Down Issues
- Heatmap Type : Heatmap is a graphical representation of Radio Frequency (RF) wireless data where the values taken by variable are represented in maps as colors. The current heatmap is computed based on the RSSI prediction model, antenna orientation, and AP transmit power. From the Heatmap Type drop-down list, select the heatmap type:
- None
- AP RSSI : Coverage heatmap, which identifies the strength of wireless signal in the specific band.
- RSSI Cut off (dBm) : Drag the slider to set the RSSI cutoff level. The RSSI cutoff ranges from -60 dBm to -90 dBm.
- Heatmap Opacity (%) : Drag the slider between 0 to 100 to set the heatmap opacity.
- Heatmap Color Scheme : The color green indicates good heatmap coverage, and the color red indicates poor heatmap coverage.
- Map Opacity (%) : Drag the slider to set the map opacity.
The AP details are reflected on the map immediately. Hover your cursor over the AP icon on the map to view AP details, RX neighbors details, client details, and switch information.
View Options for Sensors
Click the Sensors button to view sensors on the map. Expand the Sensors panel to configure these settings:
- Display Label : From the drop-down list, choose a text label that you want to view on the floor map for the selected access point. The available display labels are:
- None
- Name : Sensor name.
- Sensor MAC Address : Sensor MAC address.
View Options for Overlay Objects
Expand the Overlay Objects panel to configure these settings. Use the On/Off buttons to view these overlay objects on the map.
- Coverage Areas
- Location Regions
- Obstacles
- Rails
- Markers
Configure Map Properties
Expand the Map Properties panel to configure:
- Auto Refresh —Provides an interval drop-down list to set how often you want to refresh maps data from the database. From the Auto Refresh drop-down list, set the time intervals: None , 1 min , 2 mins , 5 mins , or 15 mins .
Configure Global Map Properties
Expand the Global Map Properties panel to configure:
- Unit of Measure —From the drop-down list, set the dimension measurements for maps to either Feet or Meters .
Filter Device Data in a Network Hierarchy Map
For 2D wireless maps, you can apply various filters to access points and sensors. Click Data in the map toolbar to begin. Based on the filter criteria, the search results appear in a table.
Manage Inventory
The Inventory function retrieves and saves details, such as host IP addresses, MAC addresses, and network attachment points about devices in its database.
About Inventory
The Inventory function retrieves and saves details, such as host IP addresses, MAC addresses, and network attachment points about devices in its database.
The Inventory feature can also work with the Device Controllability feature to configure the required network settings on devices, if these settings are not already present on the device.
Inventory uses the following protocols, as required:
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP).
- IP Device Tracking (IPDT) or Switch Integrated Security Features (SISF). (IPDT or SISF must be enabled on the device.)
- LLDP Media End-point Discovery. (This protocol is used to discover IP phones and some servers.)
- Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF). For a list of devices, see Discovery Prerequisites.
After the initial discovery, Cisco DNA Center maintains the inventory by polling the devices at regular intervals. The default interval is every six hours. However, you can change this interval up to 24 hours, as required for your network environment. For more information, see Update the Device Polling Interval. Also, a configuration change in the device triggers an SNMP trap, which in turn triggers device resynchronization. Polling occurs for each device, link, host, and interface. Only the devices that have been active for less than one day are displayed. This prevents stale device data, if any, from being displayed. On average, polling 500 devices takes approximately 20 minutes.
Update the Device Polling Interval
You can update the polling interval at the global level for all devices by choosing System > Settings > Network Resync Interval or at the device level for a specific device by choosing Device Inventory . When you set the polling interval using the Network Resync Interval , that value takes precedence over the Device Inventory polling interval value.
If you do not want a device to be polled, you can disable polling.
Before you begin
Make sure that you have devices in your inventory. If not, discover devices using the Discovery feature.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Provision > Network Devices > Inventory .
Select the devices that you want to update.
Click Update Polling Interval .
From the Update Resync Interval dialog box, in the Status field, click Enabled to turn on polling or click Disabled to turn off polling.
In the Polling Time field, enter the time interval (in minutes) between successive polling cycles. Valid values are from 25 to 1440 minutes (24 hours).
The device-specific polling time supersedes the global polling time. If you set the device-specific polling time and then change the global polling time, Cisco DNA Center continues to use the device-specific polling time.
Display Information About Your Inventory
The Inventory table displays information for each discovered device. Click the column header to sort the rows in ascending order. Click the column header again to sort the rows in descending order.

To choose which columns to show or to hide in the table, click . Note that the column selection does not persist across sessions.
When you select devices and choose a different view from the Focus drop-down list, your selection persists in each new view.
By default, 25 entries are shown in the Inventory table. Click Show More to view more entries. You can view up to 200 entries in the Inventory table.
If there are more than 25 entries in the Inventory table and you choose a different view from the Focus drop-down list, the number of entries persists in each new view.
Before you begin
Make sure that you have devices in your inventory. If not, discover devices using the Discovery feature.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Provision > Network Devices > Inventory .
The Inventory window displays the device information gathered during the discovery process. The following table describes the information that is available.
Name of the device.
Click the device name to view the following device details:
Details : Displays details such as the device name, reachability status, manageability status, IP address, device model, role, uptime, site, and so on.
- View Assurance 360 : Displays the Assurance 360 window. For 360 to open, you must have installed the Assurance application.
- Interfaces
- Ethernet Ports (For all devices): Displays the operational status and administrative status of the Ethernet ports. For Cisco Catalyst 4000 Series, 6000 Series, and 9000 Series Switches and Aggregation Services Routers (ASR) 1000 Series Routers, the ports view displays the details of line cards and supervisor cards if they are available. The line card includes the details of the platform, address, serial number, role, and stack member number. The supervisor card includes the details of the part number, serial number, switch number, and slot number. The Ports table displays the operational status, admin status, type, MAC address, PoE status, speed, MTU, and Description. The table also displays the ID of the following types of VLANs:
- VLAN ID of the manufacturing-supplied default VLAN
- VLAN ID of the configured default VLAN
- VLAN ID of the configured VLAN
For Cisco Catalyst 2000, 3000, and 9000 Series Switches, either click a port in the ports view or click the port name in the Ports table to view the maximum allocated power and power drawn details of the port.
- Status : Displays the default view of Ethernet ports.
- VLANs : Displays the VLAN assigned to a particular port. VLANs view allows you to select a maximum of 5 VLANs and lists only VLANs that are associated with the port. VLANs view displays the Selected , Not Configured , Default , and VLAN color code of the VLAN port mapping.
- Port Channels : Displays the top 5 port channels configured on the device. Port channels view displays the Selected and the Port-channel color code of configured port channels on the device.
- Clear Mac Address : You can clear the MAC address of a port. Click a port in the ports view. Then, from the Port Actions drop-down list, choose Clear Mac Address .
- Port Shut : You can shut down a port. Click a port in the ports view. Then, from the Port Actions drop-down list, choose Port Shut . Click Okay in the warning message. The admin status of the port goes to Down. To make the admin status of the port Up, from the Port Actions drop-down list, choose Port No Shut . Click Okay in the warning message.
Error-disabled ports are shown in yellow. Click an error-disabled port in ports view to view the error reason. To activate an error-disabled port, clear the MAC address and shut down the port.
- The device software type must be IOS/IOS-XE to update the VLAN, add a port description, clear the MAC address, and shut down the port.
- For Wireless Controller (WLC) devices, VLAN update, clear MAC address, and port shut are not supported.
- VLAN update, clear MAC address, and port shut are supported only on access ports.
- Port shutdown disrupts traffic on the port.
- VLAN ID of the manufacturing-supplied default VLAN
- VLAN ID of the configured default VLAN
- VLAN ID of the configured VLAN
You can click the Search or Filter option to view the details of the desired VLAN.
Note Running configuration data is not supported for devices such as wireless or legacy controllers. IP address of the device.
Shows the device support level as follows:
- Supported : The device pack is tested for all applications on Cisco DNA Center . You can open a service request if any of the Cisco DNA Center functionalities for these devices do not work.
- Unsupported : All remaining Cisco and third-party devices that are not tested and certified on Cisco DNA Center . You may try out various functionalities on Cisco DNA Center for these devices, as a best effort. However, we do not expect you to raise a service request or a bug if Cisco DNA Center features do not work as expected.
- Third Party : Device pack is built by customers or business partners and goes through the certification process. Third-party devices will support base automation capabilities such as Discovery, Inventory, Topology, and so on. Cisco TAC provides an initial level of support for these devices. However, if there is a problem with the device pack, you need to contact the business partner.
The following is a list of the various statuses:
- Reachable : The device is reachable by Cisco DNA Center using SNMP, HTTP(S), and NETCONF polling.
- Ping Reachable : The device is reachable by Cisco DNA Center using ICMP polling and not reachable using SNMP, HTTP(S), and NETCONF polling.
- Unreachable : The device is not reachable using SNMP, HTTP(S), NETCONF, or ICMP polling.
Shows the device status as follows:
- Managed with green tick icon : Device is reachable and is fully managed.
- Managed with orange error icon : Device is managed with some error such as unreachable, authentication failure, missing NETCONF ports, internal error, and so on. You can hover the cursor over the error message to view more details about the error and the impacted applications.
- Unmanaged : Device cannot be reached and no inventory information was collected due to device connectivity issues.
MAC address of the device.
Cisco IOS software that is currently running on the device.
Cisco product part number.
Cisco device serial number.
Period of time that the device has been up and running.
Role assigned to each discovered device during the scan process. The device role is used to identify and group devices according to their responsibilities and placement within the network. If Cisco DNA Center is unable to determine a device role, it sets the device role to Unknown.
If you manually change the device role, the assignment remains static. Cisco DNA Center does not update the device role even if it detects a change during a subsequent device resynchronization.
If required, you can use the drop-down list in this column to change the assigned device role. The following device roles are available:
The site to which the device is assigned. Click Assign if the device is not assigned to any site. Click Choose a Site , select a site from the hierarchy, and click Save . For more information, see About Network Hierarchy.
Most recent date and time that Cisco DNA Center scanned the device and updated the database with new information about the device.
Group of related devices, such as routers, switches, hubs, or wireless controllers.
Series number of the device; for example, Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches.
The polling interval for the device. This interval can be set globally in Settings or for a specific device in Inventory. For more information, see the Cisco DNA Center Administrator Guide.
Last Sync Status
Status of the last Discovery scan for the device:
- Managed : Device is in a fully managed state.
- Partial Collection Failure : Device is in a partial collected state and not all the inventory information has been collected. Hover the cursor over the Information (i) icon to display additional information about the failure.
- Unreachable : Device cannot be reached and no inventory information was collected due to device connectivity issues. This condition occurs when periodic collection takes place.
- Wrong Credentials : If device credentials are changed after adding the device to the inventory, this condition is noted.
- In Progress : Inventory collection is occurring.
Delete a Network Device
You can delete devices from the Cisco DNA Center database, as long as they have not already been added to a site.
When you remove a wireless sensor from the inventory, the sensor is reset to the factory defaults so that when it rejoins, it gets the current configuration.
Before you begin
You must have administrator (ROLE_ADMIN) permissions and access to all devices (RBAC Scope set to ALL) to perform this procedure.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Provision > Network Devices > Inventory .
Check the check box next to the device or devices that you want to delete.
You can select multiple devices by checking additional check boxes, or you can select all the devices by checking the check box at the top of the list.
From the Actions drop-down list, choose Inventory > Delete Device .
In the Warning window, check the Config Clean-Up check box to remove the network settings and telemetry configuration from the selected device.
Confirm the action by clicking OK .
Add a Device to a Site
Adding devices to a site configures Cisco DNA Center as the Syslog an SNMP Trap Server, which enables Syslog Level 2 and configure global telemetry settings.
Procedure

In the Cisco DNA Center GUI, click the Menu icon () and choose Provision > Network Devices > Inventory .
Check the check box for the devices that you want to assign to a site.
From the Actions menu, choose Provision > Assign Device to Site .
In the Assign Device to Site slide-in pane, click the link next to the icon for the device.
In the Choose a floor slide-in pane, select the floor to assign to the device.
(Optional) If you selected multiple devices to add to the same location, you can check the Apply to All check box for the first device to assign its location to the rest of the devices.
When assigning devices to a site, if Device Controllability is enabled, a workflow is automatically triggered to push the device configuration from the site to the devices.
About Cisco ISE Configuration for Cisco DNA Center
If your network uses Cisco ISE for user authentication, you can configure Cisco DNA Center for Cisco ISE integration. This enables you to see more information about wired clients, such as the username and operating system.
Cisco ISE configuration is centralized within NCP (Network Control Platform), which enables you to configure Cisco ISE at one GUI location. The workflow for configuring Cisco ISE is as follows:

- Click the menu icon () and choose System > Settings > External Services > Authentication and Policy Servers , and enter the Cisco ISE server details.
- After the Cisco ISE server is successfully added, NCP establishes a connection with NDP (Network Data Platform) and sends the details of the pxGrid nodes, keystore, and truststore files.
- NDP uses the configuration received from NCP to establish a pxGrid session.
- NCP automatically detects pxGrid node failovers, persona moves, and communicates it to NDP.
- If there are ISE deployment changes, NDP starts a new pxGrid session with a new pxGrid ACTIVE node.
Configure Authentication and Policy Servers
Cisco DNA Center uses AAA servers for user authentication and Cisco ISE for both user authentication and access control. Use this procedure to configure AAA servers, including Cisco ISE .
Before you begin
- If you are using Cisco ISE to perform both policy and AAA functions, make sure that Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE are integrated.
- If you are using another product (not Cisco ISE ) to perform AAA functions, make sure to do the following:
- Register Cisco DNA Center with the AAA server, including defining the shared secret on both the AAA server and Cisco DNA Center .
- Define an attribute name for Cisco DNA Center on the AAA server.
- For a Cisco DNA Center multihost cluster configuration, define all individual host IP addresses and the virtual IP address for the multihost cluster on the AAA server.
NoteAlthough pxGrid 2.0 allows up to four pxGrid nodes in the Cisco ISE deployment, Cisco DNA Center releases earlier than 2.2.1.x do not support more than two pxGrid nodes. -
You must integrate Cisco DNA Center with the primary policy administration node (PAN), and enable ERS on the PAN.
NoteWe recommend that you use ERS through the PAN. However, for backup, you can enable ERS on the PSNs. - You must enable the pxGrid service on one of the Cisco ISE nodes within the distributed deployment. Although you can choose to do so, you do not have to enable pxGrid on the PAN. You can enable pxGrid on any Cisco ISE node in your distributed deployment.
- The PSNs that you configure in Cisco ISE to handle TrustSec or SD Access content and PACs must also be defined in Work Centers > Trustsec > Trustsec Servers > Trustsec AAA Servers . For more information, see the Cisco Identity Services Engine Administrator Guide.
NoteFor Cisco ISE 2.4 Patch 13, 2.6 Patch 7, and 2.7 Patch 3, if you are using the Cisco ISE default self-signed certificate as the pxGrid certificate, Cisco ISE might reject that certificate after applying those patches. This is because the older versions of that certificate have the Netscape Cert Type extension specified as the SSL server, which now fails (because a client certificate is required). This issue does not occur in Cisco ISE 3.0 and later. For more information, see the Cisco ISE Release Notes. Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose System > Settings > External Services > Authentication and Policy Servers .
From the Add drop-down list, choose AAA or ISE .
To configure the primary AAA server, enter the following information:
- Server IP Address : IP address of the AAA server.
- Shared Secret : Key for device authentications. The shared secret can contain up to 100 characters.
To configure a Cisco ISE server, enter the following details:
- Server IP Address : IP address of the ISE server.
- Shared Secret : Key for device authentications.
- Username : Username that is used to log in to the Cisco ISE CLI.
Note This user must be a Super Admin. - We recommend that you copy the FQDN that is defined in Cisco ISE ( Administration > Deployment > Deployment Nodes > List ) and paste it directly into this field.
- The FQDN that you enter must match the FQDN, Common Name (CN), or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) defined in the Cisco ISE certificate.
The FQDN consists of two parts, a hostname and the domain name, in the following format:
For example, the FQDN for a Cisco ISE server can be ise.cisco.com.
- Virtual IP Address(es) : Virtual IP address of the load balancer behind which the Cisco ISE policy service nodes (PSNs) are located. If you have multiple PSN farms behind different load balancers, you can enter a maximum of six virtual IP addresses.
Click Advanced Settings and configure the settings:
- Connect to pxGrid : Check this check box to enable pxGrid connection. If you want to use the Cisco DNA Center system certificate as the pxGrid client certificate (sent to ISE to authenticate the Cisco DNA Center system as a pxGrid client), check the Use Cisco DNA Center Certificate for pxGrid check box. You can use this option if all the certificates that are used in your operating environments must be generated by the same CA. If this option is disabled, Cisco DNA Center will send a request to Cisco ISE to generate a pxGrid client certificate for the system to use. When you enable this option, ensure that:
- The Cisco DNA Center certificate is generated by the same Certificate Authority (CA) as is in use by Cisco ISE (otherwise the pxGrid authentication will fail).
- The Certificate Extended Key Use (EKU) field includes “Client Authentication”.
Attention If you do not enable TACAS for a Cisco ISE server here, you cannot configure the Cisco ISE server as a TACACS server under Design > Network Settings > Network when configuring a AAA server for network device authentication. After the required information is provided, Cisco ISE is integrated with Cisco DNA Center in two phases. It takes several minutes for the integration to complete. The phase-wise integration status is shown in the Authentication and Policy Servers window and System 360 window as follows:
Cisco ISE server registration phase:
- Authentication and Policy Servers window: "In Progress"
- System 360 window: "Primary Available"
pxGrid subscriptions registration phase:
- Authentication and Policy Servers window: "Active"
- System 360 window: "Primary Available" and "pxGrid Available"
If the status of the configured Cisco ISE server is shown as "FAILED" due to a password change, click Retry , and update the password to resynchronize the Cisco ISE connectivity.
To add a secondary server, repeat the preceding steps.
Configure Syslog, SNMP Traps, NetFlow Collector Servers, and Wired Client Data Collection Using Telemetry
With Cisco DNA Center , you can configure global network settings when devices are assigned to a specific site. Telemetry polls network devices and collects telemetry data according to the settings in the SNMP server, the syslog server, the NetFlow Collector, or the wired client.
Before you begin
Create a site and assign a device to the site. See Create a Site in a Network Hierarchy.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose Design > Network Settings > Telemetry .
Expand the SNMP Traps area if it is not visible and do one of the following:
- Check the Cisco DNA Center as SNMP trap server check box.
- Check the Add an external SNMP trap server check box and enter the IP address of the external SNMP trap server. The selected server collects SNMP traps and messages from the network devices.
Expand the Syslogs area if it is not visible and do one of the following:
- Check the Use Cisco DNA Center as syslog server check box.
- Check the Add an external syslog server check box and enter the IP address of the external syslog server.
Expand the NetFlow area if it is not visible and do one of the following:
- Check the Use Cisco DNA Center as NetFlow collector server check box. The NetFlow configuration on the device interfaces is completed only when you enable application telemetry on the device. Select the NetFlow collector at the site level to configure the NetFlow destination server to the device.
- Check the Add an external NetFlow collector server check box and enter the IP address and port number of the NetFlow Collector server. The selected server is the destination server for NetFlow export from the network devices. If the NetFlow Collector is not selected, the application telemetry enablement will not work.
Expand the Wired Client Data Collection area and check the Monitor wired clients check box.
This selection turns on IP Device Tracking (IPDT) on the access devices of the site.
By default, IPDT is disabled for the site.
Note: You must enable IPDT to preview the CLI configuration. When provisioning a device, you can preview the CLI configuration before deploying it on device.
Expand the Wireless Controller, Access Point and Wireless Clients Health area and check the Enable Wireless Telemetry check box.
When selected, you can monitor the health of your network's wireless controller, access points, and wireless clients.
Configure Cisco AI Network Analytics Data Collection
Use this procedure to enable Cisco AI Network Analytics to export network event data from wireless controllers as well as the site hierarchy to the Cisco DNA Center .
Before you begin
- Make sure that you have the Cisco DNA Advantage software license for Cisco DNA Center . The AI Network Analytics application is part of the Cisco DNA Advantage software license.
- Make sure that you have downloaded and installed the AI Network Analytics application. See the "Download and Install Packages and Updates" topic in the Cisco Digital Network Architecture Center Administrator Guide.
- Make sure that your network or HTTP proxy is configured to allow outbound HTTPS (TCP 443) access to the following cloud hosts:
- api.use1.prd.kairos.ciscolabs.com (US East Region)
- api.euc1.prd.kairos.ciscolabs.com (EU Central Region)
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose System > Settings .
Scroll down to External Services and choose Cisco AI Analytics .
Do one of the following:
In the Success dialog box, click Okay .
(Recommended) In the AI Network Analytics window, click Download Configuration file.
Disable Cisco AI Network Analytics Data Collection
To disable Cisco AI Network Analytics data collection, you must turn off (disable) the connection to the Cisco AI Network Analytics cloud service. This will disable all of the Cisco AI Network Analytics -related features, such as AI-Driven Issues, Network Heatmap, Site Comparison, and Peer Comparison.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose System > Settings .
Scroll down to External Services and choose Cisco AI Analytics .
In the Cloud Connection area, click the button to off, such that appears.
To delete your network data from the Cisco AI Network Analytics cloud, contact the Cisco Technical Response Center (TAC) and open a support request.
(Optional) If you have misplaced your previous configuration, click Download configuration file .
Update the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base
Machine Reasoning knowledge packs are step-by-step workflows that are used by the Machine Reasoning Engine (MRE) to identify security issues and improve automated root cause analysis. These knowledge packs are continuously updated as more information is received. The Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base is a repository of these knowledge packs (workflows). To have access to the latest knowledge packs, you can either configure Cisco DNA Center to automatically update the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base on a daily basis, or you can perform a manual update.
Procedure

Click the menu icon () and choose System > Settings .
Scroll down to External Services and choose Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base .
- INSTALLED : Shows the installed version and installation date of the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base package.
When there is a new update to the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base, the AVAILABLE UPDATE area appears in the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base window, which provides the Version and Details about the update.
- AUTO UPDATE : Automatically updates the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base in Cisco DNA Center on a daily basis.
(Recommended) Check the AUTO UPDATE check box to automatically update the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base.
The Next Attempt area shows the date and time of the next update.
You can perform an automatic update only if Cisco DNA Center is successfully connected to the Machine Reasoning Engine in the cloud.
To manually update the Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base in Cisco DNA Center , do one of the following:
- Under AVAILABLE UPDATES , click Update . A Success pop-up window appears with the status of the update.
- Manually download the Machine Reason Knowledge Base to your local machine and import it to Cisco DNA Center . Do the following:
- Click Download . The Opening mre_workflow_signed dialog box appears.
- Open or save the downloaded file to the desired location in your local machine, and then click OK .
- Click Import to import the downloaded Machine Reasoning Knowledge Base from your local machine to Cisco DNA Center .
Enable Localization
You can view the Cisco DNA Center GUI screens in English (the default), Chinese, Japanese, or Korean.
To change the default language, perform the following task:
Procedure
In your browser, change the locale to one of the supported languages: Chinese, Japanese, or Korean.
Log in to Cisco DNA Center .
The GUI screens are shown in the selected language.
Role-Based Access Control Support for Assurance
Assurance supports role-based access control (RBAC), which enables a user with SUPER-ADMIN-ROLE privileges to define custom roles that permit or restrict users access to certain Assurance features.
For more information, see the "Manage Users" chapter in the Cisco DNA Center Administrator Guide.
Use this procedure to define a custom role and then assign a user to that role.
Before you begin
Only a user with SUPER-ADMIN-ROLE permissions can perform this procedure.
Procedure
Define a custom role.
To assign a user to the custom role you just created, click Add Users .
The User Management > Internal Users window appears, which allows you to assign the custom role to an existing user or to a new user.
- To assign the custom role to an existing user, do the following:
- In the Internal Users window, click the radio button next to the user to whom you want to assign the custom role, and then click Edit . The Update Internal User slide-in pane appears.
- From the Role List drop-down list, choose the custom role, and then click Save .
- To assign the custom role to a new user, do the following:
- Click + Add . The Create Internal User slide-in pane appears.
- Enter the first name, last name, and username in the fields provided.
- From the Role List drop-down list, choose the custom role to assign to the new user.
- Enter the password and then confirm it.
- Click Save .
If you are an existing user who was logged in when the administrator was making changes to your access permissions, you must log out of Cisco DNA Center and then log back in for the new permission settings to take effect.
- Ethernet Ports (For all devices): Displays the operational status and administrative status of the Ethernet ports. For Cisco Catalyst 4000 Series, 6000 Series, and 9000 Series Switches and Aggregation Services Routers (ASR) 1000 Series Routers, the ports view displays the details of line cards and supervisor cards if they are available. The line card includes the details of the platform, address, serial number, role, and stack member number. The supervisor card includes the details of the part number, serial number, switch number, and slot number. The Ports table displays the operational status, admin status, type, MAC address, PoE status, speed, MTU, and Description. The table also displays the ID of the following types of VLANs: