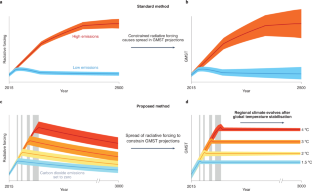
Since the Paris Agreement, the impacts of 1.5 and 2 °C global warming have been emphasized, but the rate of warming also has regional effects. A new framework of model experiments is needed to increase our understanding of climate stabilization and its impacts.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions critical to limit climate tipping risks
- Tessa Möller
- , Annika Ernest Högner
- … Nico Wunderling
Nature Communications Open Access 01 August 2024
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
206,07 € per year
only 17,17 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
References
- Seneviratne, S. I., Donat, M. G., Pitman, A. J., Knutti, R. & Wilby, R. L. Nature529, 477–483 (2016). ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Tebaldi, C. & Knutti, R. Environ. Res. Lett.13, 055006 (2018). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Schleussner, C.-F. et al. Earth Syst. Dyn.7, 327–351 (2016). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sanderson, B. M. et al. Earth Syst. Dyn.8, 827–847 (2017). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell, D. et al. Geosci. Model Dev.10, 571–583 (2017). ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Rogelj, J., Schleussner, C.-F. & Hare, W. Geophys. Res. Lett.44, 10662–10665 (2017). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Manabe, S., Stouffer, R. J., Spelman, M. J. & Bryan, K. J. Clim.4, 785–818 (1991). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Rugenstein, M. et al. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc.100, 2551–2570 (2019). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Rugenstein, M. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett.47, e2019GL083898 (2020). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- King, A. D., Lane, T. P., Henley, B. J. & Brown, J. R. Nat. Clim. Chang.10, 42–47 (2020). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sigmond, M., Fyfe, J. C., Saenko, O. A. & Swart, N. C. Nat. Clim. Chang.10, 672–677 (2020). ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Sniderman, J. M. K. et al. Nat. Clim. Chang.9, 232–236 (2019). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Hawkins, E. & Sutton, R. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc.90, 1095–1108 (2009). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jones, C. D. et al. Geosci. Model Dev.12, 4375–4385 (2019). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Callahan, C. W. et al. Nat. Clim. Chang.11, 752–757 (2021). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mohtadi, M., Prange, M. & Steinke, S. Nature533, 191–199 (2016). ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- MacDougall, A. H. et al. Biogeosciences17, 2987–3016 (2020). ArticleGoogle Scholar
Acknowledgements
A.D.K. was funded by the Australian Research Council (DE180100638). J.M.K.S. was funded by Australian Research Council grant FL160100028 to J. Woodhead. A.J.D. and E.H. were funded by the UK NERC REAL project (NE/N018591/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- School of Geography, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia Andrew D. King, J. M. Kale Sniderman & Josephine R. Brown
- ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate Extremes, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia Andrew D. King & Josephine R. Brown
- National Centre for Atmospheric Science and Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, UK Andrea J. Dittus & Ed Hawkins
- CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Aspendale, Victoria, Australia Tilo Ziehn
- Andrew D. King


